#Kubernetes Commands
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Deploying Large Language Models on Kubernetes: A Comprehensive Guide
New Post has been published on https://thedigitalinsider.com/deploying-large-language-models-on-kubernetes-a-comprehensive-guide/
Deploying Large Language Models on Kubernetes: A Comprehensive Guide
Large Language Models (LLMs) are capable of understanding and generating human-like text, making them invaluable for a wide range of applications, such as chatbots, content generation, and language translation.
However, deploying LLMs can be a challenging task due to their immense size and computational requirements. Kubernetes, an open-source container orchestration system, provides a powerful solution for deploying and managing LLMs at scale. In this technical blog, we’ll explore the process of deploying LLMs on Kubernetes, covering various aspects such as containerization, resource allocation, and scalability.
Understanding Large Language Models
Before diving into the deployment process, let’s briefly understand what Large Language Models are and why they are gaining so much attention.
Large Language Models (LLMs) are a type of neural network model trained on vast amounts of text data. These models learn to understand and generate human-like language by analyzing patterns and relationships within the training data. Some popular examples of LLMs include GPT (Generative Pre-trained Transformer), BERT (Bidirectional Encoder Representations from Transformers), and XLNet.
LLMs have achieved remarkable performance in various NLP tasks, such as text generation, language translation, and question answering. However, their massive size and computational requirements pose significant challenges for deployment and inference.
Why Kubernetes for LLM Deployment?
Kubernetes is an open-source container orchestration platform that automates the deployment, scaling, and management of containerized applications. It provides several benefits for deploying LLMs, including:
Scalability: Kubernetes allows you to scale your LLM deployment horizontally by adding or removing compute resources as needed, ensuring optimal resource utilization and performance.
Resource Management: Kubernetes enables efficient resource allocation and isolation, ensuring that your LLM deployment has access to the required compute, memory, and GPU resources.
High Availability: Kubernetes provides built-in mechanisms for self-healing, automatic rollouts, and rollbacks, ensuring that your LLM deployment remains highly available and resilient to failures.
Portability: Containerized LLM deployments can be easily moved between different environments, such as on-premises data centers or cloud platforms, without the need for extensive reconfiguration.
Ecosystem and Community Support: Kubernetes has a large and active community, providing a wealth of tools, libraries, and resources for deploying and managing complex applications like LLMs.
Preparing for LLM Deployment on Kubernetes:
Before deploying an LLM on Kubernetes, there are several prerequisites to consider:
Kubernetes Cluster: You’ll need a Kubernetes cluster set up and running, either on-premises or on a cloud platform like Amazon Elastic Kubernetes Service (EKS), Google Kubernetes Engine (GKE), or Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS).
GPU Support: LLMs are computationally intensive and often require GPU acceleration for efficient inference. Ensure that your Kubernetes cluster has access to GPU resources, either through physical GPUs or cloud-based GPU instances.
Container Registry: You’ll need a container registry to store your LLM Docker images. Popular options include Docker Hub, Amazon Elastic Container Registry (ECR), Google Container Registry (GCR), or Azure Container Registry (ACR).
LLM Model Files: Obtain the pre-trained LLM model files (weights, configuration, and tokenizer) from the respective source or train your own model.
Containerization: Containerize your LLM application using Docker or a similar container runtime. This involves creating a Dockerfile that packages your LLM code, dependencies, and model files into a Docker image.
Deploying an LLM on Kubernetes
Once you have the prerequisites in place, you can proceed with deploying your LLM on Kubernetes. The deployment process typically involves the following steps:
Building the Docker Image
Build the Docker image for your LLM application using the provided Dockerfile and push it to your container registry.
Creating Kubernetes Resources
Define the Kubernetes resources required for your LLM deployment, such as Deployments, Services, ConfigMaps, and Secrets. These resources are typically defined using YAML or JSON manifests.
Configuring Resource Requirements
Specify the resource requirements for your LLM deployment, including CPU, memory, and GPU resources. This ensures that your deployment has access to the necessary compute resources for efficient inference.
Deploying to Kubernetes
Use the kubectl command-line tool or a Kubernetes management tool (e.g., Kubernetes Dashboard, Rancher, or Lens) to apply the Kubernetes manifests and deploy your LLM application.
Monitoring and Scaling
Monitor the performance and resource utilization of your LLM deployment using Kubernetes monitoring tools like Prometheus and Grafana. Adjust the resource allocation or scale your deployment as needed to meet the demand.
Example Deployment
Let’s consider an example of deploying the GPT-3 language model on Kubernetes using a pre-built Docker image from Hugging Face. We’ll assume that you have a Kubernetes cluster set up and configured with GPU support.
Pull the Docker Image:
bashCopydocker pull huggingface/text-generation-inference:1.1.0
Create a Kubernetes Deployment:
Create a file named gpt3-deployment.yaml with the following content:
apiVersion: apps/v1 kind: Deployment metadata: name: gpt3-deployment spec: replicas: 1 selector: matchLabels: app: gpt3 template: metadata: labels: app: gpt3 spec: containers: - name: gpt3 image: huggingface/text-generation-inference:1.1.0 resources: limits: nvidia.com/gpu: 1 env: - name: MODEL_ID value: gpt2 - name: NUM_SHARD value: "1" - name: PORT value: "8080" - name: QUANTIZE value: bitsandbytes-nf4
This deployment specifies that we want to run one replica of the gpt3 container using the huggingface/text-generation-inference:1.1.0 Docker image. The deployment also sets the environment variables required for the container to load the GPT-3 model and configure the inference server.
Create a Kubernetes Service:
Create a file named gpt3-service.yaml with the following content:
apiVersion: v1 kind: Service metadata: name: gpt3-service spec: selector: app: gpt3 ports: - port: 80 targetPort: 8080 type: LoadBalancer
This service exposes the gpt3 deployment on port 80 and creates a LoadBalancer type service to make the inference server accessible from outside the Kubernetes cluster.
Deploy to Kubernetes:
Apply the Kubernetes manifests using the kubectl command:
kubectl apply -f gpt3-deployment.yaml kubectl apply -f gpt3-service.yaml
Monitor the Deployment:
Monitor the deployment progress using the following commands:
kubectl get pods kubectl logs <pod_name>
Once the pod is running and the logs indicate that the model is loaded and ready, you can obtain the external IP address of the LoadBalancer service:
kubectl get service gpt3-service
Test the Deployment:
You can now send requests to the inference server using the external IP address and port obtained from the previous step. For example, using curl:
curl -X POST http://<external_ip>:80/generate -H 'Content-Type: application/json' -d '"inputs": "The quick brown fox", "parameters": "max_new_tokens": 50'
This command sends a text generation request to the GPT-3 inference server, asking it to continue the prompt “The quick brown fox” for up to 50 additional tokens.
Advanced topics you should be aware of
While the example above demonstrates a basic deployment of an LLM on Kubernetes, there are several advanced topics and considerations to explore:
_*]:min-w-0″ readability=”131.72387362124″>
1. Autoscaling
Kubernetes supports horizontal and vertical autoscaling, which can be beneficial for LLM deployments due to their variable computational demands. Horizontal autoscaling allows you to automatically scale the number of replicas (pods) based on metrics like CPU or memory utilization. Vertical autoscaling, on the other hand, allows you to dynamically adjust the resource requests and limits for your containers.
To enable autoscaling, you can use the Kubernetes Horizontal Pod Autoscaler (HPA) and Vertical Pod Autoscaler (VPA). These components monitor your deployment and automatically scale resources based on predefined rules and thresholds.
2. GPU Scheduling and Sharing
In scenarios where multiple LLM deployments or other GPU-intensive workloads are running on the same Kubernetes cluster, efficient GPU scheduling and sharing become crucial. Kubernetes provides several mechanisms to ensure fair and efficient GPU utilization, such as GPU device plugins, node selectors, and resource limits.
You can also leverage advanced GPU scheduling techniques like NVIDIA Multi-Instance GPU (MIG) or AMD Memory Pool Remapping (MPR) to virtualize GPUs and share them among multiple workloads.
3. Model Parallelism and Sharding
Some LLMs, particularly those with billions or trillions of parameters, may not fit entirely into the memory of a single GPU or even a single node. In such cases, you can employ model parallelism and sharding techniques to distribute the model across multiple GPUs or nodes.
Model parallelism involves splitting the model architecture into different components (e.g., encoder, decoder) and distributing them across multiple devices. Sharding, on the other hand, involves partitioning the model parameters and distributing them across multiple devices or nodes.
Kubernetes provides mechanisms like StatefulSets and Custom Resource Definitions (CRDs) to manage and orchestrate distributed LLM deployments with model parallelism and sharding.
4. Fine-tuning and Continuous Learning
In many cases, pre-trained LLMs may need to be fine-tuned or continuously trained on domain-specific data to improve their performance for specific tasks or domains. Kubernetes can facilitate this process by providing a scalable and resilient platform for running fine-tuning or continuous learning workloads.
You can leverage Kubernetes batch processing frameworks like Apache Spark or Kubeflow to run distributed fine-tuning or training jobs on your LLM models. Additionally, you can integrate your fine-tuned or continuously trained models with your inference deployments using Kubernetes mechanisms like rolling updates or blue/green deployments.
5. Monitoring and Observability
Monitoring and observability are crucial aspects of any production deployment, including LLM deployments on Kubernetes. Kubernetes provides built-in monitoring solutions like Prometheus and integrations with popular observability platforms like Grafana, Elasticsearch, and Jaeger.
You can monitor various metrics related to your LLM deployments, such as CPU and memory utilization, GPU usage, inference latency, and throughput. Additionally, you can collect and analyze application-level logs and traces to gain insights into the behavior and performance of your LLM models.
6. Security and Compliance
Depending on your use case and the sensitivity of the data involved, you may need to consider security and compliance aspects when deploying LLMs on Kubernetes. Kubernetes provides several features and integrations to enhance security, such as network policies, role-based access control (RBAC), secrets management, and integration with external security solutions like HashiCorp Vault or AWS Secrets Manager.
Additionally, if you’re deploying LLMs in regulated industries or handling sensitive data, you may need to ensure compliance with relevant standards and regulations, such as GDPR, HIPAA, or PCI-DSS.
7. Multi-Cloud and Hybrid Deployments
While this blog post focuses on deploying LLMs on a single Kubernetes cluster, you may need to consider multi-cloud or hybrid deployments in some scenarios. Kubernetes provides a consistent platform for deploying and managing applications across different cloud providers and on-premises data centers.
You can leverage Kubernetes federation or multi-cluster management tools like KubeFed or GKE Hub to manage and orchestrate LLM deployments across multiple Kubernetes clusters spanning different cloud providers or hybrid environments.
These advanced topics highlight the flexibility and scalability of Kubernetes for deploying and managing LLMs.
Conclusion
Deploying Large Language Models (LLMs) on Kubernetes offers numerous benefits, including scalability, resource management, high availability, and portability. By following the steps outlined in this technical blog, you can containerize your LLM application, define the necessary Kubernetes resources, and deploy it to a Kubernetes cluster.
However, deploying LLMs on Kubernetes is just the first step. As your application grows and your requirements evolve, you may need to explore advanced topics such as autoscaling, GPU scheduling, model parallelism, fine-tuning, monitoring, security, and multi-cloud deployments.
Kubernetes provides a robust and extensible platform for deploying and managing LLMs, enabling you to build reliable, scalable, and secure applications.
#access control#Amazon#Amazon Elastic Kubernetes Service#amd#Apache#Apache Spark#app#applications#apps#architecture#Artificial Intelligence#attention#AWS#azure#Behavior#BERT#Blog#Blue#Building#chatbots#Cloud#cloud platform#cloud providers#cluster#clusters#code#command#Community#compliance#comprehensive
0 notes
Text
Install Canonical Kubernetes on Linux | Snap Store
Fast, secure & automated application deployment, everywhere Canonical Kubernetes is the fastest, easiest way to deploy a fully-conformant Kubernetes cluster. Harnessing pure upstream Kubernetes, this distribution adds the missing pieces (e.g. ingress, dns, networking) for a zero-ops experience. Get started in just two commands: sudo snap install k8s –classic sudo k8s bootstrap — Read on…
View On WordPress
#dns#easiest way to deploy a fully-conformant Kubernetes cluster. Harnessing pure upstream Kubernetes#everywhere Canonical Kubernetes is the fastest#Fast#networking) for a zero-ops experience. Get started in just two commands: sudo snap install k8s --classic sudo k8s bootstrap#secure & automated application deployment#this distribution adds the missing pieces (e.g. ingress
1 note
·
View note
Text
How to Install Kubectl on Windows 11
Kubernetes is an open-source system for automating containerized application deployment, scaling, and management. You can run commands against Kubernetes clusters using the kubectl command-line tool. kubectl can be used to deploy applications, inspect and manage cluster resources, and inspect logs. You can install Kubectl on various Linux platforms, macOS, and Windows. The choice of your…

View On WordPress
#Command Line Tool#Install Kubectl#K8#Kubectl#Kubernetes#Kubernetes Command Line Tool#Windows#Windows 11
1 note
·
View note
Text
Best Kubernetes Management Tools in 2023
Best Kubernetes Management Tools in 2023 #homelab #vmwarecommunities #Kubernetesmanagementtools2023 #bestKubernetescommandlinetools #managingKubernetesclusters #Kubernetesdashboardinterfaces #kubernetesmanagementtools #Kubernetesdashboard
Kubernetes is everywhere these days. It is used in the enterprise and even in many home labs. It’s a skill that’s sought after, especially with today’s push for app modernization. Many tools help you manage things in Kubernetes, like clusters, pods, services, and apps. Here’s my list of the best Kubernetes management tools in 2023. Table of contentsWhat is Kubernetes?Understanding Kubernetes and…

View On WordPress
#best Kubernetes command line tools#containerized applications management#Kubernetes cluster management tools#Kubernetes cost monitoring#Kubernetes dashboard interfaces#Kubernetes deployment solutions#Kubernetes management tools 2023#large Kubernetes deployments#managing Kubernetes clusters#open-source Kubernetes tools
0 notes
Text
so at work theres a kubernetes command called kgpo that is used to list pods and i just mentally call it the "kagepro" command :p
4 notes
·
View notes
Text
Exploit Me, Baby, One More Time: Command Injection in Kubernetes Log Query
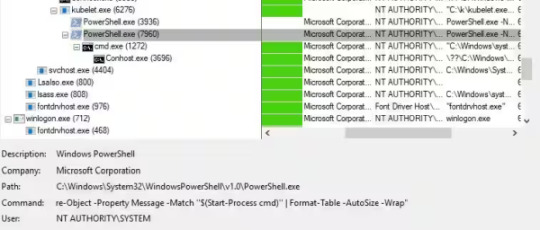
Source: https://www.akamai.com/blog/security-research/2025/jan/2024-january-kubernetes-log-query-rce-windows
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Ansible Collections: Extending Ansible’s Capabilities
Ansible is a powerful automation tool used for configuration management, application deployment, and task automation. One of the key features that enhances its flexibility and extensibility is the concept of Ansible Collections. In this blog post, we'll explore what Ansible Collections are, how to create and use them, and look at some popular collections and their use cases.
Introduction to Ansible Collections
Ansible Collections are a way to package and distribute Ansible content. This content can include playbooks, roles, modules, plugins, and more. Collections allow users to organize their Ansible content and share it more easily, making it simpler to maintain and reuse.
Key Features of Ansible Collections:
Modularity: Collections break down Ansible content into modular components that can be independently developed, tested, and maintained.
Distribution: Collections can be distributed via Ansible Galaxy or private repositories, enabling easy sharing within teams or the wider Ansible community.
Versioning: Collections support versioning, allowing users to specify and depend on specific versions of a collection. How to Create and Use Collections in Your Projects
Creating and using Ansible Collections involves a few key steps. Here’s a guide to get you started:
1. Setting Up Your Collection
To create a new collection, you can use the ansible-galaxy command-line tool:
ansible-galaxy collection init my_namespace.my_collection
This command sets up a basic directory structure for your collection:
my_namespace/
└── my_collection/
├── docs/
├── plugins/
│ ├── modules/
│ ├── inventory/
│ └── ...
├── roles/
├── playbooks/
├── README.md
└── galaxy.yml
2. Adding Content to Your Collection
Populate your collection with the necessary content. For example, you can add roles, modules, and plugins under the respective directories. Update the galaxy.yml file with metadata about your collection.
3. Building and Publishing Your Collection
Once your collection is ready, you can build it using the following command:
ansible-galaxy collection build
This command creates a tarball of your collection, which you can then publish to Ansible Galaxy or a private repository:
ansible-galaxy collection publish my_namespace-my_collection-1.0.0.tar.gz
4. Using Collections in Your Projects
To use a collection in your Ansible project, specify it in your requirements.yml file:
collections:
- name: my_namespace.my_collection
version: 1.0.0
Then, install the collection using:
ansible-galaxy collection install -r requirements.yml
You can now use the content from the collection in your playbooks:--- - name: Example Playbook hosts: localhost tasks: - name: Use a module from the collection my_namespace.my_collection.my_module: param: value
Popular Collections and Their Use Cases
Here are some popular Ansible Collections and how they can be used:
1. community.general
Description: A collection of modules, plugins, and roles that are not tied to any specific provider or technology.
Use Cases: General-purpose tasks like file manipulation, network configuration, and user management.
2. amazon.aws
Description: Provides modules and plugins for managing AWS resources.
Use Cases: Automating AWS infrastructure, such as EC2 instances, S3 buckets, and RDS databases.
3. ansible.posix
Description: A collection of modules for managing POSIX systems.
Use Cases: Tasks specific to Unix-like systems, such as managing users, groups, and file systems.
4. cisco.ios
Description: Contains modules and plugins for automating Cisco IOS devices.
Use Cases: Network automation for Cisco routers and switches, including configuration management and backup.
5. kubernetes.core
Description: Provides modules for managing Kubernetes resources.
Use Cases: Deploying and managing Kubernetes applications, services, and configurations.
Conclusion
Ansible Collections significantly enhance the modularity, distribution, and reusability of Ansible content. By understanding how to create and use collections, you can streamline your automation workflows and share your work with others more effectively. Explore popular collections to leverage existing solutions and extend Ansible’s capabilities in your projects.
For more details click www.qcsdclabs.com
#redhatcourses#information technology#linux#containerorchestration#container#kubernetes#containersecurity#docker#dockerswarm#aws
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Navigating the DevOps Landscape: Your Comprehensive Guide to Mastery
In today's ever-evolving IT landscape, DevOps has emerged as a mission-critical practice, reshaping how development and operations teams collaborate, accelerating software delivery, enhancing collaboration, and bolstering efficiency. If you're enthusiastic about embarking on a journey towards mastering DevOps, you've come to the right place. In this comprehensive guide, we'll explore some of the most exceptional resources for immersing yourself in the world of DevOps.

Online Courses: Laying a Strong Foundation
One of the most effective and structured methods for establishing a robust understanding of DevOps is by enrolling in online courses. ACTE Institute, for instance, offers a wide array of comprehensive DevOps courses designed to empower you to learn at your own pace. These meticulously crafted courses delve deep into the fundamental principles, best practices, and practical tools that are indispensable for achieving success in the world of DevOps.
Books and Documentation: Delving into the Depth
Books serve as invaluable companions on your DevOps journey, providing in-depth insights into the practices and principles of DevOps. "The Phoenix Project" by the trio of Gene Kim, Kevin Behr, and George Spafford is highly recommended for gaining profound insights into the transformative potential of DevOps. Additionally, exploring the official documentation provided by DevOps tool providers offers an indispensable resource for gaining nuanced knowledge.
DevOps Communities: Becoming Part of the Conversation
DevOps thrives on the principles of community collaboration, and the digital realm is replete with platforms that foster discussions, seek advice, and facilitate the sharing of knowledge. Websites such as Stack Overflow, DevOps.com, and Reddit's DevOps subreddit serve as vibrant hubs where you can connect with fellow DevOps enthusiasts and experts, engage in enlightening conversations, and glean insights from those who've traversed similar paths.
Webinars and Events: Expanding Your Horizons
To truly expand your DevOps knowledge and engage with industry experts, consider attending webinars and conferences dedicated to this field. Events like DevOpsDays and DockerCon bring together luminaries who generously share their insights and experiences, providing you with unparalleled opportunities to broaden your horizons. Moreover, these events offer the chance to connect and network with peers who share your passion for DevOps.
Hands-On Projects: Applying Your Skills
In the realm of DevOps, practical experience is the crucible in which mastery is forged. Therefore, seize opportunities to take on hands-on projects that allow you to apply the principles and techniques you've learned. Contributing to open-source DevOps initiatives on platforms like GitHub is a fantastic way to accrue real-world experience, all while contributing to the broader DevOps community. Not only do these projects provide tangible evidence of your skills, but they also enable you to build an impressive portfolio.
DevOps Tools: Navigating the Landscape
DevOps relies heavily on an expansive array of tools and technologies, each serving a unique purpose in the DevOps pipeline. To become proficient in DevOps, it's imperative to establish your own lab environments and engage in experimentation. This hands-on approach allows you to become intimately familiar with tools such as Jenkins for continuous integration, Docker for containerization, Kubernetes for orchestration, and Ansible for automation, to name just a few. A strong command over these tools equips you to navigate the intricate DevOps landscape with confidence.
Mentorship: Guiding Lights on Your Journey
To accelerate your journey towards DevOps mastery, consider seeking mentorship from seasoned DevOps professionals. Mentors can provide invaluable guidance, share real-world experiences, and offer insights that are often absent from textbooks or online courses. They can help you navigate the complexities of DevOps, provide clarity during challenging moments, and serve as a source of inspiration. Mentorship is a powerful catalyst for growth in the DevOps field.

By harnessing the full spectrum of these resources, you can embark on a transformative journey towards becoming a highly skilled DevOps practitioner. Armed with a profound understanding of DevOps principles, practical experience, and mastery over essential tools, you'll be well-equipped to tackle the multifaceted challenges and opportunities that the dynamic field of DevOps presents. Remember that continuous learning and staying abreast of the latest DevOps trends are pivotal to your ongoing success. As you embark on your DevOps learning odyssey, know that ACTE Technologies is your steadfast partner, ready to empower you on this exciting journey. Whether you're starting from scratch or enhancing your existing skills, ACTE Technologies Institute provides you with the resources and knowledge you need to excel in the dynamic world of DevOps. Enroll today and unlock your boundless potential. Your DevOps success story begins here. Good luck on your DevOps learning journey!
9 notes
·
View notes
Text
Inside the World of Full Stack Development: Crafting Seamless Digital Experiences
In today’s fast-paced digital age, the demand for adaptable, versatile developers has reached an all-time high. As businesses continue to evolve in a technology-driven landscape, the role of full stack developers has emerged as a pivotal force in shaping seamless digital experiences. From the front-end visuals to the back-end functionality, these professionals orchestrate entire applications with precision and efficiency.
But what does it really mean to live inside the world of full stack development?
Understanding the Full Stack Ecosystem
Full stack development refers to the ability to work on both the front end and back end of web and software applications. While front-end development focuses on user interface (UI) and user experience (UX), the back end includes server logic, databases, APIs, and integration systems.
To craft a seamless digital experience, a full stack developer must have a working command over multiple layers of technology. A few core components include:
Front-end technologies such as HTML, CSS, JavaScript, React, or Angular.
Back-end development using tools like Node.js, Python, Ruby, or Java.
Database management with MySQL, MongoDB, or PostgreSQL.
Version control systems like Git for code management.
Server and deployment practices using Docker, Kubernetes, or AWS.
But mastering tools isn’t enough. What truly sets apart today’s developers is how they learn and apply these skills in real-time environments.
Project-Based Full Stack Learning: The Key to Practical Expertise
Traditional learning models often focus too much on theory. But in the evolving tech ecosystem, practical exposure wins the race. This is where project-based full stack learning steps in.
Instead of merely learning syntax or reading documentation, learners build actual applications that reflect real-world use cases. This method:
Encourages hands-on coding from day one.
Teaches students how different components interact in a live environment.
Helps learners grasp error handling, debugging, and optimization organically.
Boosts confidence and provides a portfolio to showcase in interviews.
In short, it bridges the gap between conceptual understanding and workplace application.
Solving Real-World Challenges with Java
A core part of being a well-rounded full stack developer is problem-solving. And Java, being one of the most stable and widely-used programming languages, plays a crucial role in that journey.
Real-time problem-solving with Java introduces developers to scenarios where high-performance, secure, and scalable systems are required. Think of things like:
Building payment gateways
Developing REST APIs for e-commerce platforms
Creating server-side logic for mobile applications
Ensuring thread safety and memory management in multi-user systems
Using Java in full stack development isn’t just about writing back-end logic; it’s about integrating robust performance and security within scalable architectures. And when these solutions are executed in real-time, they provide a rich learning ground for both novices and seasoned developers.
Why Full Stack Development Matters Today
Crafting seamless digital experiences isn't simply about attractive interfaces. It's about delivering responsive, secure, and optimized platforms that feel effortless to users.
Here’s why full stack development has become a cornerstone in the tech world:
Efficiency: One person can handle both front and back-end, reducing development time and communication gaps.
Flexibility: Developers can switch roles depending on project needs.
Comprehension: Better understanding of how components interact improves debugging and integration.
Value: Companies save costs while ensuring faster delivery and consistency.
In fact, many startups and small businesses now prefer hiring full stack developers over segmented teams, as they can iterate rapidly and pivot when needed.
Building a Career Inside the Full Stack World
To thrive in this space, aspiring developers must combine technical skills with the right mindset. Here’s what helps:
Focus on end-to-end project development. Not just coding snippets, but building from concept to deployment.
Practice debugging in live environments. Mistakes are your best teachers.
Engage in real-time problem-solving with Java and other back-end tools.
Join developer communities. Platforms like GitHub, Stack Overflow, and Dev.to offer immense collaborative learning.
Stay updated. The tech world evolves fast — full stack developers must keep up.
Top Skills Every Full Stack Developer Should Master
HTML5, CSS3, JavaScript (ES6+)
Front-end frameworks like React, Vue, or Angular
Back-end platforms like Node.js, Java Spring Boot, or Express.js
Databases: SQL & NoSQL
Version Control: Git & GitHub
Web Hosting & Deployment: Heroku, AWS, Netlify
Soft Skills: Communication, Time Management, and Critical Thinking
Final Thoughts
Inside the world of full stack development, the journey is as important as the destination. From learning through project-based full stack learning modules to encountering real-time problem-solving with Java, the process transforms a beginner into a professional equipped to handle dynamic digital challenges.
Crafting seamless digital experiences isn’t just about code — it’s about vision, innovation, and adaptability. Full stack developers are not just builders of websites or apps; they are the architects of digital transformation.
Whether you're a curious beginner or a tech enthusiast looking to upskill, stepping into this world is a decision that will shape not just your career, but the way you understand and influence technology.
0 notes
Text
Best cloud computing courses
Empower Your Career with Sunshine Learning: The Best IT Training Institute in India
In the rapidly evolving digital landscape, acquiring specialized IT skills is no longer optional—it’s essential. Whether you’re a student, a working professional, or a career switcher, selecting the right training partner can make all the difference. That’s where Sunshine Learning steps in. Recognized as a leading IT training institute in India, we are committed to helping you build a strong foundation and master the latest technologies through practical, real-world training programs.
Why Choose Sunshine Learning?
Sunshine Learning is more than just an institute; it’s a community of learners, educators, and industry professionals passionate about technology and innovation. Our curriculum is carefully designed to bridge the gap between academic knowledge and industrial demand. With a team of certified trainers, hands-on labs, and job-oriented content, we provide a comprehensive learning experience that prepares you for global opportunities.
Our learning philosophy focuses on flexibility, depth, and industry relevance, ensuring that every student emerges job-ready. We offer instructor-led live training, self-paced modules, and weekend bootcamps to suit your learning style and schedule.
Industry-Relevant IT Courses
At Sunshine Learning, we offer a wide array of courses across trending technologies, including cloud computing, DevOps, cybersecurity, data science, and more. Whether you're a beginner aiming to understand IT fundamentals or a professional seeking advanced certifications, we have tailored training paths for everyone.
Our programs are designed to offer:
Interactive live classes
Real-time project experience
Resume building and interview preparation
Certification assistance
Best Cloud Computing Courses with Real-Time Projects
One of the flagship programs at Sunshine Learning is our best cloud computing courses. Cloud computing has transformed the way businesses operate, and professionals skilled in this domain are in high demand.
Our cloud courses cover:
Fundamentals of cloud computing
Public vs. private vs. hybrid cloud models
Major platforms: AWS, Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud GCP
What sets us apart is our project-based learning. Students work on live projects and real-world case studies, gaining practical exposure to cloud infrastructure setup, storage solutions, and deployment techniques.
Special Focus: Google Cloud GCP Course
If you're looking to specialize in Google Cloud GCP course, Sunshine Learning provides an in-depth, hands-on program that equips you with the skills to design, develop, and manage dynamic solutions using GCP.
This course is ideal for:
System administrators
Solution architects
Cloud engineers
IT professionals aiming for GCP certification
Key highlights:
Google Cloud fundamentals and core services
Identity and access management (IAM)
Kubernetes and App Engine deployments
Real-time projects with Google Cloud console
Certification test prep for Google Associate and Professional exams
Why Cloud Skills Matter More Than Ever
Organizations across the globe are moving their operations to the cloud. According to Gartner, over 85% of businesses will adopt a cloud-first strategy by 2026. Professionals with cloud certifications command higher salaries and better job security. Whether you're aiming for a role in cloud development, architecture, security, or DevOps, investing in a robust cloud education is a wise move.
With Sunshine Learning, you not only learn cloud computing, but also gain confidence to work in real-world production environments.
Student Success Stories
Thousands of learners have upskilled through our platform and transitioned into high-paying IT roles. Here are a few examples:
Anjali S., a graduate from Pune, completed our cloud computing course and secured a job at an MNC as a Cloud Solutions Engineer.
Ramesh K., an experienced system admin, took our Google Cloud GCP course and cleared his Professional Cloud Architect certification on the first attempt.
Their success is a testament to the quality of training we offer at Sunshine Learning.
Career Support & Placement Assistance
Enrolling in Sunshine Learning doesn’t just mean accessing premium content. It also means gaining a career partner. We offer:
One-on-one career counselling
Resume review and optimization
Mock interviews with cloud experts
Placement support with hiring partners
This holistic approach ensures you're not just trained but also employable.
Learn Anytime, Anywhere
All our courses are accessible through an intuitive learning management system (LMS), allowing you to learn anytime, anywhere. We understand the constraints of working professionals and students, and hence provide options like weekend classes, recorded sessions, and 24x7 support.
Whether you're located in Delhi, Mumbai, Bangalore, or a remote town in India, Sunshine Learning brings top-quality IT education to your doorstep.
0 notes
Text
Latest Trends in DevOps Services for Cloud Migration (2025)

Cloud migration in 2025 is being shaped by a convergence of advanced DevOps practices and emerging technologies. Here are the most significant trends:
Hybrid and Multi-Cloud Strategies
Organizations are increasingly adopting hybrid and multi-cloud environments to avoid vendor lock-in, optimize workloads, and enhance redundancy. Modern DevOps consulting services are focusing on seamless transitions between on-premises, private, and multiple public clouds, leveraging advanced orchestration tools to automate deployments and ensure compatibility across diverse platforms.
AI-Driven Optimization
Artificial Intelligence is revolutionizing cloud migration. AI-powered tools analyze workloads for optimal placement, predict migration issues, and provide real-time insights for dynamic resource allocation. Post-migration, AI continues to monitor and optimize cloud environments, ensuring ongoing performance and cost efficiency.
Serverless and Cloud-Native DevOps
The adoption of serverless computing and cloud-native architectures is accelerating. Serverless CI/CD pipelines and tools like Kubernetes and Docker are enabling microservices-based deployments, allowing teams to focus on application logic while infrastructure management is automated and scalable.
GitOps and Infrastructure as Code (IaC)
GitOps is becoming a core practice, allowing infrastructure and application code to be managed in version-controlled repositories. This approach ensures consistency, auditability, and rapid recovery, and integrates smoothly with CI/CD and DevSecOps workflows.
Enhanced Security and DevSecOps
Security is being integrated earlier in the migration process through DevSecOps. Advanced security protocols, including Zero Trust Architecture, end-to-end encryption, and AI-driven threat detection, are now standard to protect data and ensure compliance during and after migration.
Cost-Efficiency and FinOps
Migration services are adopting cost-optimization strategies, such as subscription-based pricing and containerization. FinOps practices are being integrated to provide visibility into cloud expenses and help organizations manage and optimize spending.
Sustainability Initiatives
Eco-friendly practices are gaining prominence. Providers are investing in green data centers, carbon footprint monitoring, and sustainable migration processes to address the environmental impact of cloud computing.
Collaboration and Communication Tools
Enhanced collaboration is being facilitated by ChatOps and integrated communication platforms, allowing real-time troubleshooting and deployment commands within familiar messaging interfaces, thus improving agility and response times.
Continuous Improvement and Post-Migration Optimization
DevOps emphasizes continuous monitoring, incident management, and iterative optimization after migration. This ensures that cloud environments are always aligned with business goals and performance expectations.
These trends reflect a holistic approach to cloud migration, where DevOps is not just about automation but also about intelligence, security, sustainability, and collaboration, ensuring organizations achieve agility, resilience, and cost-effectiveness in their cloud journeys.
0 notes
Text
CompTIA Linux+: Opening Doors to a Career in Linux Systems
In the world of IT, Linux is a cornerstone operating system, driving countless systems from servers and cloud platforms to mobile devices and embedded systems. For those aiming to build a career in systems administration, DevOps, or cloud computing, mastering Linux skills is essential. The CompTIA Linux+ certification is designed to provide professionals with the foundational skills needed to manage Linux systems, setting them up for success in various IT roles. This blog will take a closer look at what the CompTIA Linux+ certification is, the skills it covers, and why it’s a valuable asset for aspiring IT professionals.
What is CompTIA Linux+?
CompTIA Linux+ is a vendor-neutral certification that validates core Linux administration skills. Designed for IT professionals who want to build proficiency in Linux systems, this certification covers everything from basic command-line functions and scripting to system security, user management, and troubleshooting. It’s particularly beneficial for anyone who plans to work in server administration, cloud computing, or cybersecurity, as Linux remains the preferred OS for many high-demand technologies.

Why Pursue CompTIA Linux+?
Here’s why the CompTIA Linux+ certification is valuable for today’s IT professionals:
1. High Demand for Linux Skills
Linux powers more than 90% of the world’s supercomputers and is a dominant force in servers, cloud platforms, and data centers. In addition, open-source software and Linux are integral to DevOps practices, containerization (like Docker and Kubernetes), and network security. CompTIA Linux+ prepares you for this wide-ranging demand by covering essential Linux skills that can be applied across these sectors.
2. A Practical, Hands-On Certification
CompTIA Linux+ focuses on practical skills. The exam includes performance-based questions, which require candidates to demonstrate their knowledge by solving real-world problems rather than just answering multiple-choice questions. This hands-on approach ensures that certified professionals are prepared for the day-to-day challenges they’ll encounter in a Linux-based environment.
3. Foundation for Advanced Linux Certifications
While CompTIA Linux+ is an entry-level certification, it’s also a solid foundation for more specialized or advanced Linux certifications, such as the Red Hat Certified System Administrator (RHCSA) or Linux Foundation Certified Engineer (LFCE). By building a foundation with Linux+, professionals can confidently pursue these advanced certifications to enhance their career prospects.
4. Versatility Across Industries
Linux is used extensively in fields like web hosting, cloud services, telecommunications, and embedded systems. CompTIA Linux+ can qualify you for various roles, including Linux Administrator, Systems Administrator, Network Engineer, DevOps Engineer, and Cloud Engineer. These roles are highly adaptable, and a strong foundation in Linux can help you seamlessly transition across different IT domains.
Key Skills Covered by CompTIA Linux+
The CompTIA Linux+ certification covers a comprehensive set of skills, ensuring professionals have the knowledge required to perform essential Linux administration tasks. Here’s a breakdown of some of the key areas:
1. System Configuration and Management
Candidates learn how to configure and manage Linux systems, from the command line to setting up essential services. This includes working with package managers to install and update software, configuring the boot process, and managing partitions and filesystems. These skills are critical for maintaining system performance and stability.
2. Command-Line Proficiency
The command line is at the heart of Linux, and CompTIA Linux+ emphasizes proficiency in various command-line tools. Candidates learn commands for managing files, processes, and permissions, as well as advanced text processing tools. Command-line skills are essential for troubleshooting, automating tasks, and managing systems efficiently.
3. User and Group Management
CompTIA Linux+ teaches the skills required to create, manage, and secure user accounts and groups. This includes understanding permissions, setting up secure authentication, and configuring access controls. These skills are crucial for ensuring system security and protecting sensitive data.
4. Networking and Security
The certification covers essential networking concepts, such as configuring IP addresses, setting up network interfaces, and troubleshooting network issues. In addition, Linux+ emphasizes security practices, such as configuring firewalls, implementing secure shell (SSH) connections, and managing access controls. These skills ensure that systems remain secure and protected against potential threats.
5. Scripting and Automation
Automation is key to managing systems at scale, and CompTIA Linux+ includes an introduction to shell scripting. Candidates learn how to write and execute scripts to automate repetitive tasks, making them more efficient and effective in their roles. This skill is especially valuable for those pursuing careers in DevOps or systems administration.
CompTIA Linux+ Exam Details
The CompTIA Linux+ certification requires passing a single exam:
Exam Code: XK0–005
Number of Questions: Up to 90
Question Format: Multiple-choice and performance-based
Duration: 90 minutes
Passing Score: 720 (on a scale of 100–900)
The exam is divided into four main domains:
System Management (32%)
Security (21%)
Scripting, Automation, and Programming (19%)
Troubleshooting (28%)
These domains ensure that candidates are well-rounded in their Linux knowledge and can apply their skills in practical, real-world scenarios.
Tips for Passing the CompTIA Linux+ Exam
Get Comfortable with the Command Line: Linux+ requires command-line proficiency, so spend plenty of time practicing common commands and scripts.
Use Hands-On Practice Labs: Set up a Linux environment at home or use a virtual machine to practice. There are also online labs and simulators available that mimic real-world Linux environments.
Review the Exam Objectives: CompTIA provides a list of objectives for the Linux+ exam. Make sure you’re familiar with each topic, as the exam is structured around these domains.
Take Practice Exams: Practice exams will give you a feel for the question formats and identify any areas that need more attention.
Learn Scripting Basics: Since automation is a part of the exam, make sure you understand the fundamentals of shell scripting. Even basic scripts can save time and demonstrate your efficiency in managing Linux systems.
Conclusion
The CompTIA Linux+ certification is a valuable asset for IT professionals seeking to build a career in Linux administration, DevOps, or cloud computing. With Linux’s wide application across industries, Linux+ provides a flexible foundation for a variety of IT roles, from system administration to cybersecurity.
0 notes
Text
SRE Roadmap: Your Complete Guide to Becoming a Site Reliability Engineer in 2025
In today’s rapidly evolving tech landscape, Site Reliability Engineering (SRE) has become one of the most in-demand roles across industries. As organizations scale and systems become more complex, the need for professionals who can bridge the gap between development and operations is critical. If you’re looking to start or transition into a career in SRE, this comprehensive SRE roadmap will guide you step by step in 2025.

Why Follow an SRE Roadmap?
The field of SRE is broad, encompassing skills from DevOps, software engineering, cloud computing, and system administration. A well-structured SRE roadmap helps you:
Understand what skills are essential at each stage.
Avoid wasting time on non-relevant tools or technologies.
Stay up to date with industry standards and best practices.
Get job-ready with the right certifications and hands-on experience.
SRE Roadmap: Step-by-Step Guide
🔹 Phase 1: Foundation (Beginner Level)
Key Focus Areas:
Linux Fundamentals – Learn the command line, shell scripting, and process management.
Networking Basics – Understand DNS, HTTP/HTTPS, TCP/IP, firewalls, and load balancing.
Version Control – Master Git and GitHub for collaboration.
Programming Languages – Start with Python or Go for scripting and automation tasks.
Tools to Learn:
Git
Visual Studio Code
Postman (for APIs)
Recommended Resources:
"The Linux Command Line" by William Shotts
GitHub Learning Lab
🔹 Phase 2: Core SRE Skills (Intermediate Level)
Key Focus Areas:
Configuration Management – Learn tools like Ansible, Puppet, or Chef.
Containers & Orchestration – Understand Docker and Kubernetes.
CI/CD Pipelines – Use Jenkins, GitLab CI, or GitHub Actions.
Monitoring & Logging – Get familiar with Prometheus, Grafana, ELK Stack, or Datadog.
Cloud Platforms – Gain hands-on experience with AWS, GCP, or Azure.
Certifications to Consider:
AWS Certified SysOps Administrator
Certified Kubernetes Administrator (CKA)
Google Cloud Professional SRE
🔹 Phase 3: Advanced Practices (Expert Level)
Key Focus Areas:
Site Reliability Principles – Learn about SLIs, SLOs, SLAs, and Error Budgets.
Incident Management – Practice runbooks, on-call rotations, and postmortems.
Infrastructure as Code (IaC) – Master Terraform or Pulumi.
Scalability and Resilience Engineering – Understand fault tolerance, redundancy, and chaos engineering.
Tools to Explore:
Terraform
Chaos Monkey (for chaos testing)
PagerDuty / OpsGenie
Real-World Experience Matters
While theory is important, hands-on experience is what truly sets you apart. Here are some tips:
Set up your own Kubernetes cluster.
Contribute to open-source SRE tools.
Create a portfolio of automation scripts and dashboards.
Simulate incidents to test your monitoring setup.
Final Thoughts
Following this SRE roadmap will provide you with a clear and structured path to break into or grow in the field of Site Reliability Engineering. With the right mix of foundational skills, real-world projects, and continuous learning, you'll be ready to take on the challenges of building reliable, scalable systems.
Ready to Get Certified?
Take your next step with our SRE Certification Course and fast-track your career with expert training, real-world projects, and globally recognized credentials.
0 notes
Text
Kubectl get context: List Kubernetes cluster connections
Kubectl get context: List Kubernetes cluster connections @vexpert #homelab #vmwarecommunities #KubernetesCommandLineGuide #UnderstandingKubectl #ManagingKubernetesResources #KubectlContextManagement #WorkingWithMultipleKubernetesClusters #k8sforbeginners
kubectl, a command line tool, facilitates direct interaction with the Kubernetes API server. Its versatility spans various operations, from procuring cluster data with kubectl get context to manipulating resources using an assortment of kubectl commands. Table of contentsComprehending Fundamental Kubectl CommandsWorking with More Than One Kubernetes ClusterNavigating Contexts with kubectl…

View On WordPress
#Advanced kubectl commands#Kubectl config settings#Kubectl context management#Kubectl for beginners#Kubernetes command line guide#Managing Kubernetes resources#Setting up kubeconfig files#Switching Kubernetes contexts#Understanding kubectl#Working with multiple Kubernetes clusters
0 notes
Text
Docker Tutorial for Beginners: Learn Docker Step by Step
What is Docker?
Docker is an open-source platform that enables developers to automate the deployment of applications inside lightweight, portable containers. These containers include everything the application needs to run—code, runtime, system tools, libraries, and settings—so that it can work reliably in any environment.
Before Docker, developers faced the age-old problem: “It works on my machine!” Docker solves this by providing a consistent runtime environment across development, testing, and production.
Why Learn Docker?
Docker is used by organizations of all sizes to simplify software delivery and improve scalability. As more companies shift to microservices, cloud computing, and DevOps practices, Docker has become a must-have skill. Learning Docker helps you:
Package applications quickly and consistently
Deploy apps across different environments with confidence
Reduce system conflicts and configuration issues
Improve collaboration between development and operations teams
Work more effectively with modern cloud platforms like AWS, Azure, and GCP
Who Is This Docker Tutorial For?
This Docker tutorial is designed for absolute beginners. Whether you're a developer, system administrator, QA engineer, or DevOps enthusiast, you’ll find step-by-step instructions to help you:
Understand the basics of Docker
Install Docker on your machine
Create and manage Docker containers
Build custom Docker images
Use Docker commands and best practices
No prior knowledge of containers is required, but basic familiarity with the command line and a programming language (like Python, Java, or Node.js) will be helpful.
What You Will Learn: Step-by-Step Breakdown
1. Introduction to Docker
We start with the fundamentals. You’ll learn:
What Docker is and why it’s useful
The difference between containers and virtual machines
Key Docker components: Docker Engine, Docker Hub, Dockerfile, Docker Compose
2. Installing Docker
Next, we guide you through installing Docker on:
Windows
macOS
Linux
You’ll set up Docker Desktop or Docker CLI and run your first container using the hello-world image.
3. Working with Docker Images and Containers
You’ll explore:
How to pull images from Docker Hub
How to run containers using docker run
Inspecting containers with docker ps, docker inspect, and docker logs
Stopping and removing containers
4. Building Custom Docker Images
You’ll learn how to:
Write a Dockerfile
Use docker build to create a custom image
Add dependencies and environment variables
Optimize Docker images for performance
5. Docker Volumes and Networking
Understand how to:
Use volumes to persist data outside containers
Create custom networks for container communication
Link multiple containers (e.g., a Node.js app with a MongoDB container)
6. Docker Compose (Bonus Section)
Docker Compose lets you define multi-container applications. You’ll learn how to:
Write a docker-compose.yml file
Start multiple services with a single command
Manage application stacks easily
Real-World Examples Included
Throughout the tutorial, we use real-world examples to reinforce each concept. You’ll deploy a simple web application using Docker, connect it to a database, and scale services with Docker Compose.
Example Projects:
Dockerizing a static HTML website
Creating a REST API with Node.js and Express inside a container
Running a MySQL or MongoDB database container
Building a full-stack web app with Docker Compose
Best Practices and Tips
As you progress, you’ll also learn:
Naming conventions for containers and images
How to clean up unused images and containers
Tagging and pushing images to Docker Hub
Security basics when using Docker in production
What’s Next After This Tutorial?
After completing this Docker tutorial, you’ll be well-equipped to:
Use Docker in personal or professional projects
Learn Kubernetes and container orchestration
Apply Docker in CI/CD pipelines
Deploy containers to cloud platforms
Conclusion
Docker is an essential tool in the modern developer's toolbox. By learning Docker step by step in this beginner-friendly tutorial, you’ll gain the skills and confidence to build, deploy, and manage applications efficiently and consistently across different environments.
Whether you’re building simple web apps or complex microservices, Docker provides the flexibility, speed, and scalability needed for success. So dive in, follow along with the hands-on examples, and start your journey to mastering containerization with Docker tpoint-tech!
0 notes